Dear readers,
Liver is one of the important organs in the body. It plays a vital role in digestion, detoxification and fat metabolism. Today we see many people are diagnosed with fatty liver. What exactly is the fatty liver? Let us understand in simple words.
Fatty liver is excessive deposition of fat (triglycerides) in liver cells (due to increase in import of fat and reduction in export of fat).
Fatty liver is of two types.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD).
Let us understand NAFLD in Ayurvedic perspective in detail.
Before that take a look at the following charts to understand it in brief with conventional medicine.
Fatty liver occurs by two ways- 1. Excess fat which increases workload on liver 2. Damaged liver cells that cannot metabolize fat properly.

Ayurveda and NAFLD:
In Ayurveda liver is termed as Yakrut. Its genesis is said to be from rakt dhatu. It is the seat of rakt dhatu & ranjak pitta. Aacharyas state that yakrut is the organ where ras dhatu is transformed into rakt dhatu. There are 7 dhatus (tissues) in the body. These dhatus are nourished one after another in given sequence (ras-rakt-mamsa-med-asthi-majja-shukra). This process of nourishment starts in the yakrut. If the nourishment of earlier dhatus doesn’t take place properly, then the rest of the dhatus stay malnourished. This leads to rog utpatti (manifestation of disease).
As we discussed in earlier blogs, Agni (can corelate with digestion and metabolism) is the main factor contributing health of an individual. Agni present in these dhatus carries out the nourishment and transformation process. When imbalance of dhatus occurs as a result of wrong food and life style, Agni present in dhatus gets weak (dhatwagnimandya) and symptoms occurs as per involvement of dhatus.
Whenever there is rog utpatti, main factors responsible are-
jatahragnimandya(weak digestive fire)
dhatwagnimandya (poor enzyme and /or hormonal activities)
vitiated doshas and blockage of strotasas (circulating channels).
In Fatty Liver, 3 major contributors are-
jatharagnimandya (weak digestive fire)
dhatwagnimandya (ras, rakt, med dhatus involved predominantly)
Kapha dosha predominant and vata, pitta get involved later.
Strotasas involved – annavaha, rasvaha, raktavaha, ambuvaha, medovaha and purishvaha strotasas.
Causes–
Dushtikaranas of these strotasas- (ref- Charak vimanstan/5)
Annavaha- अतिमात्रस्य च अकाले अहितस्य च भोजनात् | अन्नवाहिनी दुष्यंति वैगुण्यात् पावकस्य च ||
Rasvaha– गुरुशीतम् अतिस्निग्धम् अतिमात्रम् समश्नताम् | रसवाहिनी दुष्यंति चिंत्यानां च अति चिंतनात् ||
Raktavaha- विदाही अन्नपानानि स्निग्ध उष्णानि द्रवाणि च| रक्तवाहिनी दुष्यन्ति भजताम् च आतपानलौ ||
Medovaha- अव्यायामात् दिवास्वप्नात् मेदयानांचातिभक्षणात् | मेदोवाहिनी दुष्यंति वारुण्याश्च अतिसेवनात् ||
Purishvaha- विधारणात् अत्यशनात् अजीर्ण अध्यशनात् तथा | वर्चोवाहिनी दुष्यंति दुर्बलाग्ने: कृशस्य च ||
The causes mentioned in above shlokas cover almost all major lifestyle and diet habits that cause fatty liver. See the chart below.

Ayurvedic
Pathology-
Fatty liver is considered as a lifestyle disorder.
Due to wrong lifestyle, food habits and stress, kapha and meda gets vitiated.
Then,
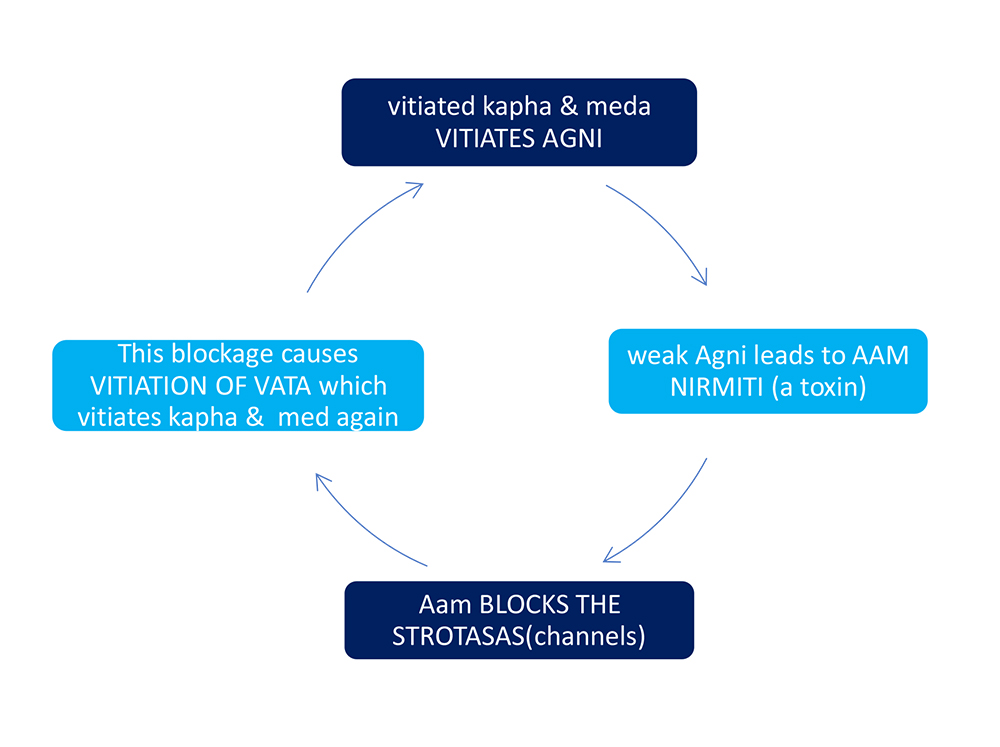
This cycle repeats itself and vitiation of kapha leads to unequal distribution of med in yakrut. Many a times pitta gets vitiated as a result of vitiation of agni and shotha lakshanas (inflammatory changes) occur.
Symptoms-
अनन्नाभिलाषणम्, अरोचक, अविपाकौ छर्दि……(lack of appetite, indigestion, vomiting etc)
अश्रद्धा अरुचि च आस्यवैरस्यम् अरसज्ञता (loss of appetite, loss of taste, having different taste)
ह्रल्लासो गौरवं तंद्रा सांगमर्दो ज्वरस्तम: (nausea, heaviness in abdomen / body, body ache, fever etc)
पांडुत्वं स्त्रोतसाम् रोध:…….. (anaemia, blockage of circulating channels [blood flow])
कुष्ठविसर्पपिडका रक्तपित्तं असृग्दर: .. कामला……. (haematemesis/ per rectum bleeding, jaundice)
अधिमांस अर्बुदम् ….. पूतिमांस….. (Growth, tumour or necrosis of cells of that particular organ)
कृच्छेण अल्पाल्पं सशब्दशूलं अतिद्रवं अतिग्रथितमतिबहु मलप्रवृत्ति (variations in bowel habits like scanty/excess quantity, painful defecation, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, etc)
Treatment-
No specific treatment protocol is there in conventional medicine. They advise weight management, diet changes as per metabolic condition, exercise and few symptomatic drugs along with hepatoprotective and antioxidant drugs.
In Ayurveda, following protocol is followed generally.

Treatment mainly involves diet and life style changes. We often think medicine is important than diet, life style corrections. In case of initial stage of fatty liver, these corrections become very important to reverse the condition. First two stages of fatty liver are reversible only if proper diet, exercise and sleep pattern is maintained along with basic medication.
Ayurveda suggests very good medicines to treat different stages. But this medication should be decided as per patient’s constitution, mental condition, age, gender and present lifestyle. commonly used medicines are aarogyavardhini vati, phalatrikadi churna/ phalatrikadi guggulu, neem, guduchi, kalmegh, pippali, punarnava, turmeric, bhoomyamalaki, kumari aasava, rohitakarishta etc.
Some diet tips-
DON’TS:
Refined flour/maida
Sugar and milk-based sweets
Tea/ coffee/alcohol
Full cream milk, ghee in excess quantity, curd
Black gram(udad), sesame seeds
Refined oil, butter, cheese
Spicy, oily/fatty food
Preserved and processed and canned food
Bakery products
Overuse of fermented products like idli, dosa
DO’S:
Vegetables: tomatoes, carrot, onion, beet root, spinach and other green leafy vegetables, mint, all gourds (bitter gourd, ridge gourd, snake gourd, bottle gourd, ivy gourd), okra, green peas, pumpkin, sprouts & occasionally cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli
Cereals: brown rice, whole oats, all millets (ragi, jowar, bajra, etc), barley, whole wheat occasionally.
Pulses: green gram, Bengal gram, red lentils, soyabean, chick peas, pigeon peas,
Spices: ginger, garlic, pepper, dry ginger, cinnamon
Fruits: pomegranate, apple, grapes, melons, berries (strawberries, blueberries), pineapple, papaya, fig, lemon & citrus fruits occasionally
Nuts-seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flax seeds, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds
Dairy: desi cow milk (if not available take toned milk), fresh buttermilk, desi cow’s ghee (A2 ghee) maximum 1 teaspoon a day, paneer
Hot beverages: green tea (ginger + lemon; lemon grass tea; tulasi + shunthi; cinnamon+ lemon+ pepper etc), Kashaya.
Prefer use of cold pressed oil/ olive oil for cooking.
Hope this blog has given you idea how important healthy liver is. No matter how busy you are, manage your diet and lifestyle in a healthy way. Take professional help if needed. Do not consume any of the above ayurvedic medicines without an ayurvedic doctor’s consent. Stay healthy and stay safe.











Thank for good information , it will definitely help full for all .